How to Prevent Asset Failures During Peak Food & Beverage Manufacturing
Equipment failures during peak production periods pose a serious threat to food and beverage manufacturing, with unplanned downtime costing the industry approximately $260,000 per hour and triggering fulfillment delays that both affect production targets and compromising customer relations. The average production disruption during peak season costs $10 million in direct expenses, with companies facing weak traceability systems experiencing costs that increase by 70%, making every unexpected equipment breakdown a potential business catastrophe.
This article examines how preventing asset failures during peak production in food and beverage manufacturing through CMMS control transforms scattered maintenance practices into verified protection through CMMS in food production, preventing downtime, and the food safety compliance systems that keep production running at full capacity.
Maintaining Asset Reliability Through Maintenance Scheduling and Documentation
Peak production depends on maintenance tasks being done on time, documented properly, and aligned with sanitation workflows that prevent equipment failure. Missed preventive maintenance, inconsistent tasks, or gaps in recordkeeping create avoidable failure risks that manifest as recalls. This is apparent just from the number of total recalls in the first three quarters of 2025 compared to annual totals for the last two years:
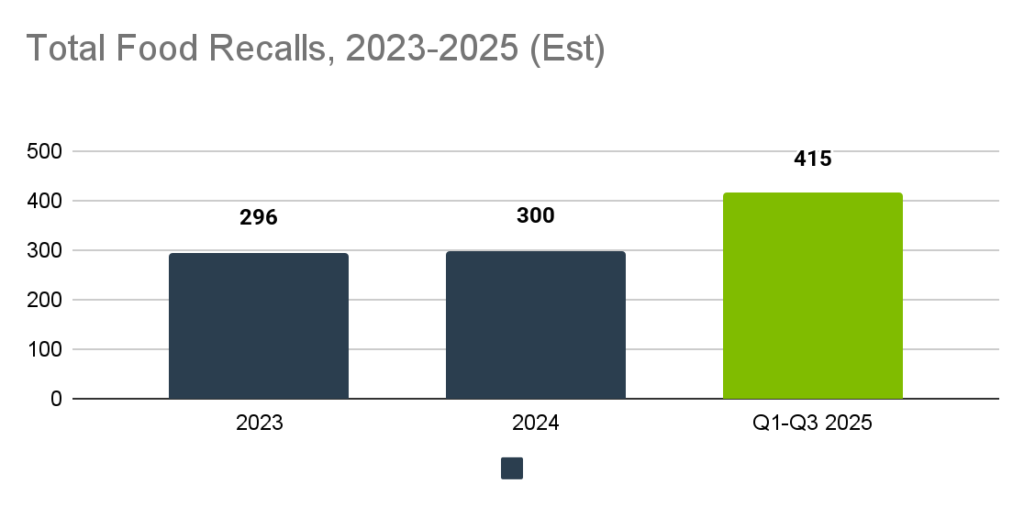
*2025 data is incomplete as of the time of writing (12/15/2025)
A comprehensive maintenance management platform gives food and beverage plants structured schedules and traceable records that support reliable peak-season production through maintenance scheduling that aligns with production requirements. This integrated approach ensures cleaning validation occurs on schedule while creating the audit-ready documentation regulators expect during food safety auditing inspections.
Ready to see for yourself? Test Drive LLumin CMMS+ to experience firsthand how improving allergen control in food and beverage manufacturing is just a click away.
How Maintenance Influences Peak Production Reliability
Preventive Maintenance Tasks Prevent Peak-Season Failures
Many equipment failure risks arise when critical preventive maintenance tasks are delayed beyond safe intervals. Equipment components that experience high stress (e.g., gaskets, conveyor belts, mixing paddles) require regular replacement and cleaning to prevent catastrophic failure between production runs. This is particularly important since, as of 2025, the FDA measures aspects like allergen contamination remains the leading cause of recalls.
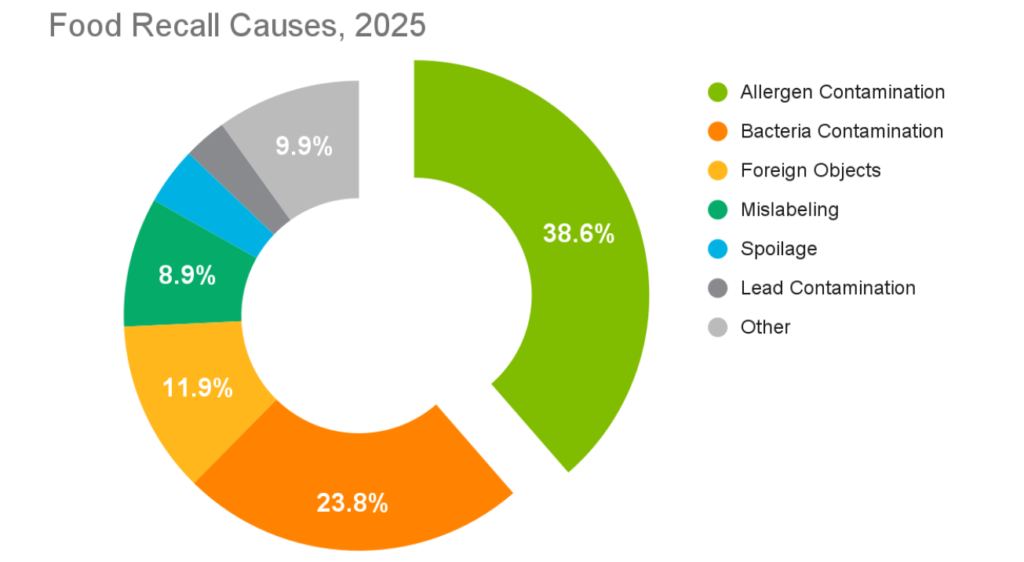
Maintenance teams need a scheduling system that prevents overdue tasks and flags high-risk equipment before production begins through preventive maintenance for overworked equipment. Modern platforms automate these preventive maintenance tasks and provide food safety teams with visibility to verify line readiness, ensuring production bottleneck analysis identifies equipment requiring attention before production issues arise.
Maintenance Timing Protects Production Windows
High production relies on strict sequencing of production, workflows, and maintenance activities that cannot overlap without creating downtime. When maintenance is done at the wrong time, food safety teams lose time restarting equipment and must repeat sanitation procedures.
| Scheduling Conflict | Impact on Production | Integrated Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance During Production | Introduces downtime risk | Calendar integration prevents overlap |
| Sanitation Before PM Complete | Servicing incomplete equipment | Sequential task dependencies |
| Emergency Repairs Mid-Run | Breaks production protocols | Rapid response without protocol breaches |
| Cross-Shift Coordination | Information gaps at handover | Continuous digital visibility |
Sophisticated systems align maintenance calendars with production schedules to prevent overlap through the integration of comprehensive workflows. This coordination ensures ingredient segregation protocols remain intact while maintenance activities occur only during validated windows that don’t compromise output goals.
Eliminate downtime risks before they become a crisis
When maintenance and production scheduling work from the same real-time schedule, the risk of unexpected failures disappears, and compliance becomes automatic. LLumin CMMS+ gives you the synchronized workflows and complete documentation, ensuring production is operating at peak capacity from start to finish.
Equipment Conditions Influence Peak Season Failures
Wear, loose fittings, and degraded seals create failure points that manifest suddenly under the stress of peak production loads. Without consistent upkeep, equipment becomes less effective even when established procedures are followed precisely. Industry analysis shows that equipment running at 90%-100% capacity during peak periods experience failure rates 3-5x higher than during normal operations with worn components finally succumbing to the continuous stress
Equipment Contamination Frequency & Impact
| Metric | Finding |
|---|---|
| Typical food processing downtime annually | 442 hours/year |
| Food manufacturers experiencing unplanned downtime | 80%+ in last 3 years |
| Equipment failure as #1 risk to production targets | 43.5% (plant level) |
| Inadequate lubrication as failure cause | 35-40% of equipment failures |
| Bearing failures from poor maintenance | ~36% of all bearing failures |
| Downtime reduction through predictive maintenance | 25-40% improvement |
Source 1 | Source 2 | Source 3
5 CMMS Tools That Support Reliable Peak-Production Workflows
1) Standard Procedures for Peak-Critical Equipment
Peak production reliability plans rely on precise, validated procedures that must be followed identically every time equipment is inspected or serviced for high-capacity production. Paper instructions are difficult to maintain, rarely updated consistently across shifts, and frequently ignored when technicians rely on experience over documentation.
During peak production,k when temporary staff or overtime shifts are common, standardized digital procedures become even more critical, reducing the “tribal knowledge” gap that causes failures when experienced technicians aren’t available.
| Procedure Element | Paper-Based Systems | Embedded Digital SOPs |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Accessibility | Binders in office, not at equipment | Mobile access at the point of work |
| Version Control | Multiple versions in circulation | Single authoritative digital source |
| Completion Verification | Assumed, rarely verified | Mandatory digital sign-off |
| Training Documentation | Separate records, gaps common | Integrated competency tracking |
Comprehensive systems embed digital SOPs into every work order so technicians follow the exact required steps through standardized procedures that ensure consistency. This approach supports production capacity targets by ensuring maintenance meets the standards necessary for equipment to operate at rated capacity to remain valid.
2) Records That Support Inspections and Investigations
Food safety teams need reliable proof that equipment was maintained, cleaned, and verified before production, which effectively serves as evidence that paper logs rarely provide consistently across shifts and sites.
On the other hand, Isolated logs make verification slow and create gaps that raise risk during audits when inspectors demand immediate evidence. During peak production, when ever hour of uptime matters, the inability to quickly verify equipment readiness can delay production starts by hours while teams manually compile maintenance history from scattered sources.
| Documentation Need | Fragmented Manual Records | Integrated Digital System |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Cleaning Logs | Scattered across clipboards and files | Centralized database with timestamps |
| Equipment Condition Results | Lab reports filed separately | Linked to equipment and batch records |
| Technician Certifications | HR files, unknown to maintenance | Verified competency for allergen work |
| Investigation Evidence | Days compiling from multiple sources | Instant retrieval during incidents |
Modern platforms capture who completed each task, when it happened, and what was verified in a connected system through corrective action documentation. This comprehensive recordkeeping supports food safety compliance requirements while accelerating hazard reporting when potential issues arise.
3) Traceability Across Maintenance and Production
When equipment fails unexpectedly, teams must quickly see which equipment, batches, and production areas were involved to contain exposure. Without a unified record, investigations are slow and often inconclusive, allowing contaminated products to remain in distribution longer. The average food recall costs $10 million in direct expenses, but companies with weak traceability systems face costs that increase by 70% due to extended investigation times.
| Traceability Element | Siloed Systems | Unified CMMS Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment-to-Batch Linkage | Manual reconstruction required | Automated batch changeover logging |
| Maintenance Verification Evidence | Multiple systems, incomplete | Complete cleaning validation records |
| Ingredient Contact History | Unknown or uncertain | Detailed ingredient segregation tracking |
| Personnel Involvement | Unclear who performed tasks | Complete technician accountability |
Sophisticated systems consolidate these records, giving maintenance and food safety teams a single source of truth through equipment traceability, which accelerates investigations. This integration ensures that every batch maintains complete documentation from raw materials through to the finished product, supporting the rapid response capabilities that regulators increasingly demand.
4) Automated Alerts That Highlight Peak-Season Risks in Real Time
Production capacity drops when unexpected equipment issues, overdue maintenance, or missed cleaning validations go unnoticed until production has already begun. A digital maintenance platform can flag these risks automatically by monitoring schedules, outstanding tasks, and condition-based indicators tied to performance. During peak production periods, the cost of missing warning signs multiples; a motor showing vibration issues, for example, might run for weeks before failure normally while only lasting 24-48 hours under peak conditions.
| Risk Alert Type | Detection Without CMMS | Automated CMMS Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Overdue Sanitation Tasks | Discovered during production | Prevented through escalation alerts |
| Failed Cleaning Verification | Found during quality review | Immediate notification to supervisors |
| Equipment Condition Decline | Becomes apparent after failure | Early warning through trend analysis |
| Expired Certifications | Technicians work without authorization | Automatic workforce qualification tracking |
Advanced platforms send real-time alerts to maintenance and food safety teams when risk factors occur through automated risk notifications. This proactive approach transforms even something like allergen management from reactive crisis response into preventive risk mitigation through hazard reporting systems that catch issues before production begins.
5) Equipment Histories That Reveal Patterns Linked to Peak-Season Failures
Equipment failure issues often trace back to repeated mechanical faults, worn components, or recurring performance challenges that aren’t obvious day to day without systematic data collection. A comprehensive system can reveal these patterns by linking maintenance work, corrective actions, and inspection results to specific equipment through pattern identification that manual systems cannot achieve.
| Pattern Recognition | Manual Analysis Limitations | CMMS Analytical Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat Failures | Not connected across time | Trend charts identify equipment problems |
| Mechanical Wear Correlation | Isolated incidents appear random | Links wear and tear to peak season failures |
| Shift-Based Variations | Blamed on personnel differences | Reveals procedure gaps or training needs |
| Seasonal Equipment Performance | Historical knowledge lost | Multi-year data reveal environmental factors |
Modern platforms help teams identify trends that contribute to peak-season failures, so they can correct root causes rather than react to individual incidents through root cause analysis. This analytical capability elevates maintenance from a reactive function to a strategic production/safety partner through continuous improvement, systematically reducing risks.
Master Reliable Production Through Proactive Maintenance
Reactive cleaning and maintenance create the gaps where equipment failure thrives. Discover how leading food manufacturers use systematic approaches to eliminate cross-contact and maintain continuous compliance.
Ensure Reliable Production with LLumin CMMS+
Peak-season production requires disciplined maintenance timing, accurate documentation, and predictable workflows that function consistently across every shift and production line. A connected maintenance system ensures that these tasks are performed consistently across the plant, eliminating the need for manual oversight that can create gaps.
LLumin CMMS+ gives food and beverage manufacturers the structure required for safe, compliant operations through Food and Beverage Manufacturing Software designed specifically for industry needs. The platform’s emphasis on digital maintenance records and preventive maintenance proof ensures operations meet the rigorous standards that protect consumer health while maintaining production efficiency.
Request a demo to see how LLumin CMMS+ can support your peak-season operations through maintenance and quality integration, transforming compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does CMMS software support peak-season production?
CMMS software supports maximized output control by automating preventive maintenance schedules that prevent equipment degradation, maintaining complete cleaning validation records, linking sanitation workflows with production calendars, and creating traceable documentation for investigations. Unplanned downtime costs manufacturers an average of $260,000 per hour, underscoring the importance of systematic equipment reliability.
How does a CMMS help verify equipment readiness before production starts?
A CMMS helps verify equipment conditions by requiring digital completion of cleaning checklists, capturing photo evidence of serviced equipment, tracking test results linked to specific equipment, and preventing production start until verification is complete. Peak production periods operate on razor-thin margins where even 30 minutes of unexpected downtime can cascade into hours of delays,m emphasizing the critical importance of verified equipment readiness. LLumin CMMS+ ensures no equipment enters production without confirmed operational readiness clearance.
Which CMMS features support peak-critical equipment?
Key CMMS features for include condition-based maintenance triggers that prevent degradation, equipment-specific maintenance procedures with mandatory completion, tracking of equipment testing with trend analysis, and automated alerts when equipment conditions risk failure under load. Companies with weak traceability face costs that increase by 70% during recalls. LLumin CMMS+ provides specialized tools that address the unique challenges of equipment reliability in food production.
How does LLumin CMMS+ help during equipment failures investigations?
LLumin CMMS+ helps during failures investigations by providing instant access to complete equipment histories, linking maintenance records to specific production shifts, showing which personnel performed verification, and revealing patterns across multiple failure events. For example, 98% of foodborne illnesses in 2024 came from just 13 outbreaks, demonstrating how single equipment failures can cascade. The platform’s unified traceability accelerates root cause identification and prevention decisions.
Why is digital documentation essential for peak production management?
Digital documentation is essential because 72% of manufacturers experience increased equipment failures during peak periods, with paper-based maintenance systems contributing to 35% of these failures through missed tasks and incomplete documentation. Digital systems provide timestamped proof of cleaning, automated validation tracking, complete traceability from ingredient to finished product, and instant evidence retrieval during audits. LLumin CMMS+ transforms maintenance documentation from a compliance burden into automated proof of food safety.
